About DME
About DME
Diabetic Macular Edema (DME), is a complication of diabetes that involves swelling in the back of the eye, in an area of the retina called the macula.1 ‘Edema’ or ‘Oedema’ are alternative spellings for the same term, meaning ‘swelling’. Hence, you may see DME referred to as DMO.
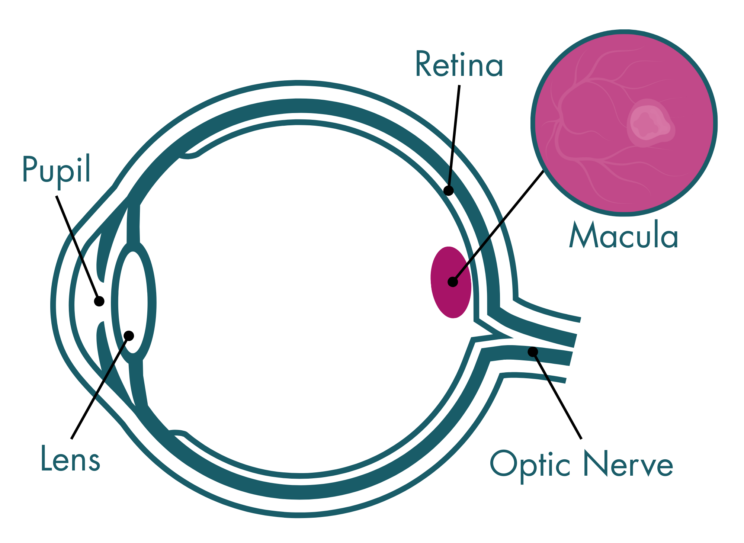
DME is a ‘complication’, as opposed to a stand-alone condition, because it develops from another disease— diabetes. DME can affect those with Type I or Type II diabetes. Affecting a third of all patients, DME is the leading cause of blindness in young adults in developed countries.2,3
References
- NHS. Patient Information - Diabetic Macular Oedema. Available at: https://elht.nhs.uk/application/files/1216/2256/2541/Diabetic_Macular_Oedema_leaflet.pdf. Last accessed April 2025.
- Macular Society. Diabetic macular oedema (DMO). Available at: https://www.macularsociety.org/macular-disease/macular-conditions/diabetic-macular-oedema/. Last accessed April 2025.
- Romero-Aroca, Pedro. “Managing diabetic macular edema: The leading cause of diabetes blindness.” World journal of diabetes vol. 2,6 (2011): 98-104. doi:10.4239/wjd.v2.i6.98.