Treatment
The loss of sight from RVO can resolve without the need for treatment. If your symptoms persist, then RVO treatment will address the swelling in the macula, as well as prevent future blockages of the retinal blood vessels.
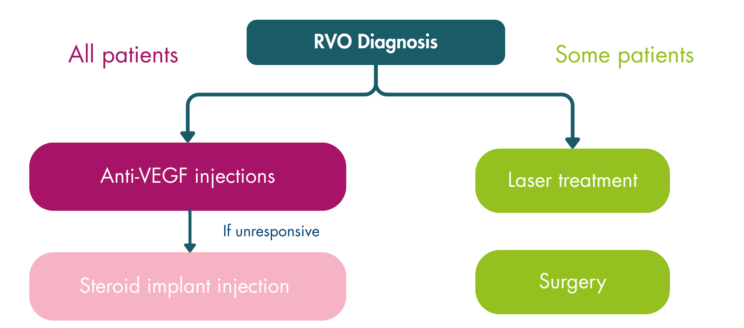
Swelling in the macula is treated similarly, regardless of the cause, using a biologic medicine called anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF).1
Biologic medicines refer to medicines made from a biological source, such as living cells and organisms. “Biosimilars” is another term that may be used when talking about biologics. Biosimilars are biological medicines which are highly similar to the original biologic reference medicine in terms of quality, safety and efficacy. This means there is no clinically meaningful difference to the original biologic medicine.
These biologic medications are given as an injection into your eye, which is called an intravitreal injection. An antiseptic solution will be used to clean your eye, and anaesthetic drops will be used to numb it. You will be asked to look in one direction, and the injection is given in the opposite corner, so you are unlikely to see the needle, and it only takes a few seconds. The majority of patients will find this procedure painless, but some people may develop pain or discomfort. In some cases, you may develop an allergic reaction, but this is rare.3
Other RVO-specific treatments are available if anti-VEGF injections are unsuccessful. In this scenario, a steroid implant will be considered instead. These are given through an injection and work by reducing inflammation in the macula. Steroid implants have a high success rate, improving vision for up to 30% of patients.3
General measures
Some of these measures seek to prevent a blockage from happening again, focusing on the cause of the blockage through lifestyle changes and medications.2
- Monitoring blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol levels
- Being treated for blood pressure, blood sugar, or cholesterol levels
- Stopping smoking
- Eating healthily and exercising
References
- Macular Society. Macular disease treatments. Available at: https://www.macularsociety.org/diagnosis-treatment/treatments/. Last accessed July 2025
- NHS Foundation Trust. Retinal vein occlusion. Available at: https://www.yorkhospitals.nhs.uk/seecmsfile/?id=2333. Last accessed April 2025.
- Macular Society. Retinal vein occlusion (RVO). Available at: https://www.macularsociety.org/macular-disease/macular-conditions/retinal-vein-occlusion/. Last accessed April 2025.